seuclidean
Syntax
seuclidean(X, Y, Z)Details
Compute the standardized Euclidean distance between two numeric vectors (X and Y). X and Y are first standardized using Z, and then euclidean is called. The distance is defined as follows:
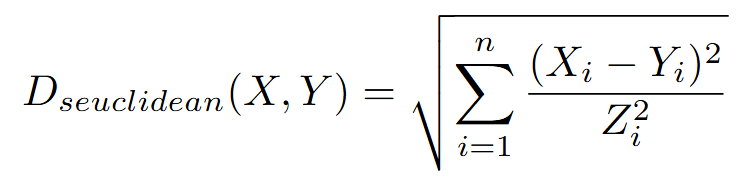
Parameters
X: A numeric vector.
Y: A numeric vector.
Z: A numeric vector representing the variance of each dimension, used for standardization.
Note:
X, Y, and Z must have the same length.
Returns
A scalar of type DOUBLE.
Examples
X = [2, 5]
Y = [3, 7]
Z = [1, 2]
seuclidean(X, Y, Z)
// Output: 1.7320508075688772Related functions
